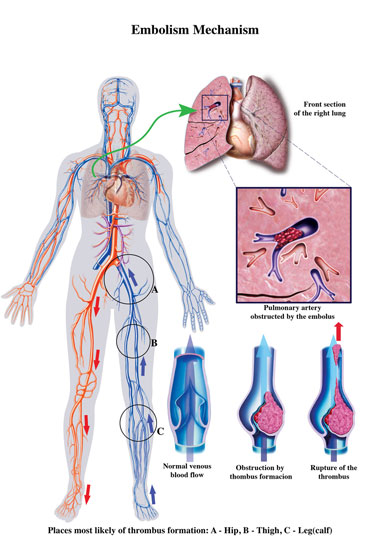
Venous Thromboembolism
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
This refers to a condition which includes Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary embolism (PE). Clots can form in the deep veins especially in the lower limbs (DVT) and subsequently there is a risk for these clots to detach from the deep veins and travel with the blood circulation, via the heart and lodge in the arteries in the lungs. This is a life-threatening condition and requires immediate medical attention.
VTE is a major cause for death and ongoing complications especially in patients admitted to hospital and also after discharge from hospital. Hence it is important to ensure that all steps are taken to reduce the risk for VTE. These measures are discussed individually under the topics of Deep vein thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism.
-
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a medical condition where one or more blood clots block the supply of blood to the lungs. The blood clot can form in the veins in the legs...
-

IVC Filter Insertion
The inferior vena cava (IVC) is the largest vein in the body (located in the abdomen) carrying impure blood from the legs and other parts of the lower body to the heart.
-
Thrombolytic Therapy
The normal process of blood clotting or coagulation occurs when platelets clump with other blood components to form a gel.
